Stimulate Hair Growth Without Sacrificing Your Sexual Performance

Are you tired of having to choose between a full head of hair and a satisfying sex life? Are you worried about sexual side effects typically associated with hair growth medications? Well, now you don’t have to. Thanks to our NEW dual-action SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance formula made with FDA-approved ingredients, such as Finasteride, Tadalafil (the same active ingredient as Cialis®), and Vitamin D3, you can stimulate hair growth without sacrificing your sexual performance by offsetting sexual side effects.
In this blog post, we’ll explore why men sometimes experience sexual side effects when taking hair growth medications, what causes erectile dysfunction (ED), and how combining these three powerful ingredients can help promote hair growth while keeping things exciting in the bedroom. We’ll also answer your questions about who this medication is for, go over any potential side effects or risks, and share some common questions we receive from patients. So, let’s dive right in!
Why Men May Experience Sexual Side Effects With Hair Growth Medications
It’s important to understand why some men may experience sexual side effects with hair growth medications and why you have avoided starting your hair growth journey. Reduced libido is a potential sexual side effect of the ingredient Finasteride and other DHT blockers, which impacts 2.1 – 3.8% of men. (1) While Finasteride is a key medication for promoting hair regrowth, it works to block the main enzymes that convert Testosterone to Dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
DHT can play a role in sexual health and function, so when Finasteride inhibits its production, some men may experience a decrease in libido or even erectile dysfunction (ED). According to a study, however, DHT may not be a vital hormone for sexual production in adult males. (2) It’s important to note that not every man taking Finasteride will experience these often temporary side effects.
What Causes Erectile Dysfunction (ED)?
Erectile dysfunction, or ED, is a condition that affects many men at some point in their lives. It means that there’s an inability to achieve or maintain an erection for sexual intercourse. ED can have various causes, both physical and psychological. The physical cause of ED is poor blood flow to the penis or genital area. ED can also be due to conditions such as high blood pressure, side effects of medications, diabetes, nerve conditions, or cardiovascular disease. When blood flow is restricted, it becomes difficult for the penis to fill with enough blood to produce an erection.
Psychological factors can also have physical effects on a man’s ability to produce an erection. Stress and anxiety, depression, or relationship issues can all interfere with sexual performance and lead to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection. Suffering from hair loss and thinning can impact confidence in and out of the bedroom. So, when hair growth medications cause ED, this only makes the emotional impact twofold. That’s why combining hair growth medications with those that offset sexual side effects can be the answer to your concerns.

The Benefits of Combining Finasteride With Tadalafil & Vitamin D3
Combining Finasteride with medications like those in our SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance, including Tadalafil and Vitamin D3, can help reduce them. While Tadalafil is commonly used to treat ED and can also be used for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), it acts as a vasodilator which may increase blood flow to the scalp and penis—which can have a dual-action benefit of promoting hair growth at the follicles and offsetting any sexual side effects at the same time. (3) A study testing the effects of PDE5 inhibitors on hair growth it showed an increase in “vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), which are responsible for hair growth.” (4)
Tadalafil works by targeting the enzyme and catalyst Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) responsible for smooth muscle movement and the leading cause of erectile dysfunction (ED). (5) Research has suggested that Vitamin D3 deficiency could be linked to hair loss and ED. (6) Combining Vitamin D3 with these ingredients, you can support healthy hair growth and improve your overall sexual response when aroused.
Potential Side Effects of Finasteride & Tadalafil
As with any new medication, you may experience some side effects. If you’re interested in taking Finasteride, the most common adverse reactions associated with the medication in a 4-year study were impotence, decreased libido, decreased ejaculation volume, breast enlargement and tenderness, and rash. (7) For those interested in taking Tadalafil, the most common adverse reactions are dizziness, upset stomach or nausea, dyspepsia, back pain, myalgia, nasal congestion, headaches, muscle aches, pain in limb, and facial flushing. Please visit our Drug Safety & Information page here for a complete list of side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions About SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance
Who is SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance for?
SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance is a formula we’ve created for men over 18 in good health. If you’re experiencing hair loss or are worried about sexual side effects, this product is perfect for you. But before beginning any new medication, we recommend speaking with your doctor.
I’m worried about sexual side effects. Will SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance help?
Good question. Some men can experience sexual side effects when using Finasteride for hair growth. However, Tadalafil (the same active ingredient in Cialis®) helps to offset those effects by boosting blood flow. The result? Dual treatment to help support hair growth and treat erectile dysfunction (ED) so there’s no interruption in arousal or performance.
How do I know if the SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance is right for me?
If you’re ready to kickstart your hair growth without sacrificing sexual performance, this may be the perfect solution for you. After completing your medical history, you’ll be connected with your Happy Head dermatologist to help answer all questions. We offer many custom hair growth solutions that you might like to try.
Are there side effects associated with Tadalafil (Cialis®)?
As with any medication, there is always a chance you may experience mild side effects such as headache, nausea, indigestion, stuffy nose, dizziness, and muscle aches. Should you experience these side effects, we recommend you stop taking the medication immediately and speak with your doctor. However, a study indicates that Tadalafil can be beneficial in “repairing damaged vascular endothelium and promoting long-term improvement of erectile function.”
How long does Tadalafil take to work in combination with hair growth ingredients like those in our SuperCapsule™?
Hair growth results typically show between 3 to 6 months. You can experience a performance boost from the Tadalafil (Cialis®) within 24-36 hours of use. Tadalafil is formulated to improve blood flow to the scalp and genital area to help improve sexual arousal response and hair growth in combination with Finasteride.
I’m already taking Viagra. Can I still take the SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance?
If you’re taking Viagra, we do not recommend you add the SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance because it contains Tadalafil (generic for Cialis®). However, you can take a different SuperCapsule™ formula for hair growth, such as our Finasteride or Dutasteride formulas. We do recommend switching from Viagra to this SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance since it works to improve both hair growth and sexual performance. Tadalafil has shown additional benefits when taken daily, compared to Viagra, which cannot be taken daily.
I sometimes get dizzy. Should I take SuperCapsule™ + ED performance if that’s an issue?
Before you begin taking any new medications, but especially if you have a history of dizziness, low blood pressure, or any heart conditions, we suggest you talk with your doctor. If you do suffer from occasional dizzy spells but are cleared to take Tadalafil (generic for Cialis®), we recommend you take the medication at night since dizziness will likely pass during sleep.
When is the best time to take SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance? In the morning or evening?
You can take our SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance at any time of the day that’s most convenient for you. However, if you experience dizziness as the product can lower your blood pressure, so we recommend you take it at night.
Should I avoid taking SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance if I’m taking heart medication?
If you are taking nitrates, we recommend you speak with your doctor before starting any new medication. Generally, you should avoid taking Tadalafil (Cialis®) if you have a history of heart attack, stroke, angina, irregular heartbeat, severe liver disease, or low blood pressure.
What’s included in the SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance?
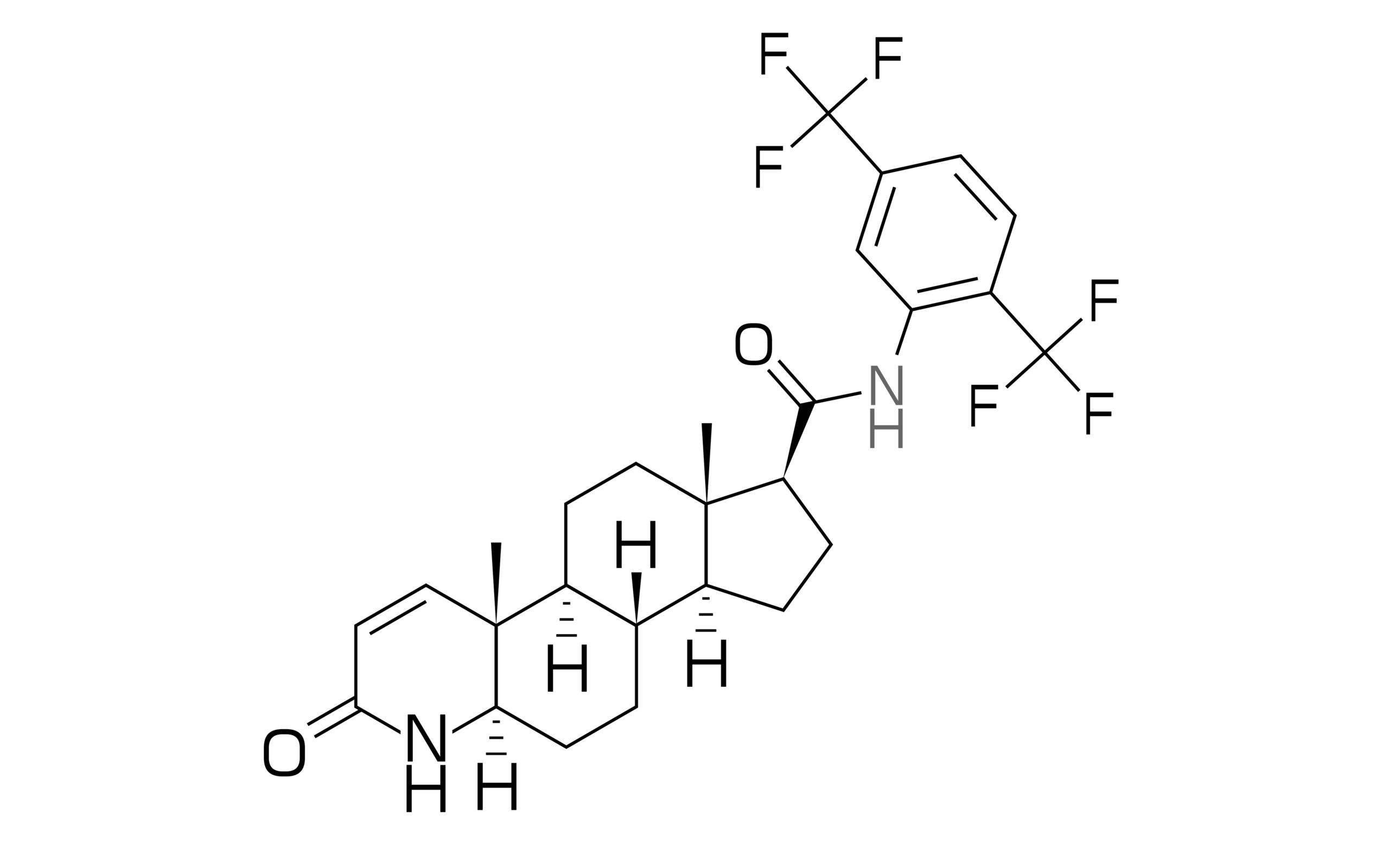
Our SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance includes 1.0 mg of Finasteride, 5.0 mg of Tadalafil, and 2,000 IU of Vitamin D3. Finasteride helps stop hair loss by targeting the enzyme that converts Testosterone to DHT. Tadalafil acts as a vasodilator, increasing blood flow to the scalp and genital area to promote hair growth and improve sexual arousal response. Vitamin D3 supports healthy hair growth and the creation of new hair follicles, along with better skin.
How does SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance offset sexual side effects that come with hair growth medications?
Tadalafil is included in this men’s formula to help offset sexual performance concerns associated with hair growth medicine while also supporting hair growth by increasing blood flow to the scalp. Tadalafil works by targeting the enzyme Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5), the leading cause of erectile dysfunction (ED).
If you want to grow your hair back but are concerned about the potential sexual side effects of hair growth medications, our SuperCapsule™ + ED Performance may be right for you. At Happy Head, you’re assigned a board-certified dermatologist to help you decide on the perfect hair growth formula to achieve results in 3 to 6 months. So, if you have any more questions and want to try it, you’re not alone on your hair growth journey.
Resources:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3481923/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24751323/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2575214/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30292404/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3776492/#:~:text=Each%20PDE%20family%20contributes%20to%20various%20physiological%20functions.&text=Because%20the%20smooth%20muscle%20of,effects%20from%20nonspecific%20PDE%20inhibition.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34553483/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006291X1832103X
- https://assets.researchsquare.com/files/rs-2281439/v1/dd2f9e8f-0bde-4c68-8894-9c1e9d619604.pdf?c=1669052658
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006291X1832103X


 As a world-renowned board-certified dermatologist, Dr. Ben Behnam answers the question of why you may experience a shedding phase once you start your hair growth treatments. Hair shedding and hair growth are two distinct, but equally important natural processes in the hair growth cycle that can happen at the same time. Understanding the difference between them can help you stick to your hair growth solutions and maintain the results you’re seeing. Dr. Ben Behnam explains everything you need to know about the differences between hair growth and shedding, in addition to understanding
As a world-renowned board-certified dermatologist, Dr. Ben Behnam answers the question of why you may experience a shedding phase once you start your hair growth treatments. Hair shedding and hair growth are two distinct, but equally important natural processes in the hair growth cycle that can happen at the same time. Understanding the difference between them can help you stick to your hair growth solutions and maintain the results you’re seeing. Dr. Ben Behnam explains everything you need to know about the differences between hair growth and shedding, in addition to understanding  Who Is Benjamin Katz?
Who Is Benjamin Katz?





