When Women Get Male Pattern Hair Loss

I met my friend Barbara (01) twelve years ago when our boys were toddlers. Barbara is a tiny woman with lots of spunk. I always thought of her as strong, smart, and confident. She called one day and confided in me that it bothered her that her hair was thinning. She had been losing hair on the crown of her head since she was in her late 20s, and she never did anything about it. She knew that I had lichen planopilaris and wanted to get the name of the dermatologist I used to treat my hair loss.
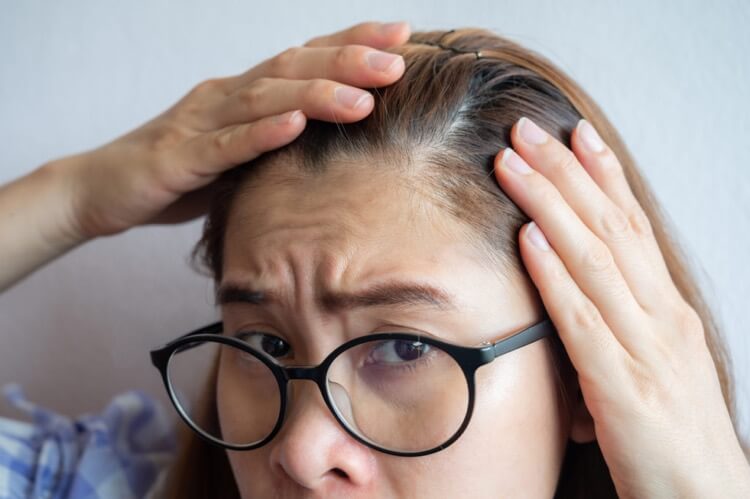
Anyone knew just from looking at Barbara that her hair was sparse, and it took me by surprise that she hadn’t already had it checked out by a dermatologist or a hair specialist. But then again, Barbara isn’t exactly a fashionista. She’s an elder care nurse who spends most of her weekdays in scrubs and her weekends in sweats. But still, I was surprised. Barbara visited my dermatologist, and it turns out that she has androgenic alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness. Who knew that women can get male pattern baldness? And who knew that it could start so young?
How Do Women Get Male Pattern Baldness?
Women get male pattern baldness for the same reasons men do. Also known as androgenic alopecia, female pattern hair loss is usually inherited. The condition occurs when a woman has a shorter than normal period of hair growth and a longer than normal period between when her hair sheds and grows. In some cases, women have the misfortune of inheriting smaller hair follicles and thinner strands of hair.
Almost every woman experiences female pattern hair loss at some point in her life. Most first notice androgenic alopecia around menopause, but it can start any time after puberty begins. If anyone on either side of your family has lost his or her hair, it’s more likely that you will too.
What Does Female Pattern Baldness Look Like?
There’s some good news if you have female pattern baldness. Women’s hairlines usually don’t recede and you won’t end up with a donut. The other good news is that women typically don’t go completely bald. Usually women with androgenic alopecia have one of three different patterns of hair loss. A bald spot can form at the crown of your head, you could lose hair along your center part, or your hair could thin all over. In some cases, hair gets so thin that the scalp can be seen.
How to Identify Male Pattern Baldness in Women
Although it’s tempting, don’t try to self-diagnose or treat yourself if you think you have androgenic alopecia. Get an appointment with a board-certified dermatologist and hair specialist. Your dermatologist may do one or several of the following:
- Evaluate your hair loss pattern
- Review your medical history
- Rule out other possible causes for your hair loss, such as iron or vitamin D deficiency, thyroid disease, or another type of scarring alopecia
- Determine whether you are producing too much androgen (male hormone)
- Use a dermoscope or a microscope to look at the structure of your hair shaft
- Take a small biopsy of your scalp and send it to a pathologist
Androgenic Alopecia Often Goes Undiagnosed in African American Women
Women of every race are affected by androgenic alopecia and other types of hair loss. African American women are no exception. In a 2016 survey conducted at Boston University’s Sloane Epidemiology Center, 47.6 percent of African-American women surveyed reported hair loss. (02)
However, like my friend Barbara who noticed that her hair was thinning and didn’t do anything about it, many African-American women are not seeking treatment for androgenic alopecia. Out of the group surveyed, 81.4 percent reported that they had never consulted with a physician about their thinning hair or bald spots.
The moral of this story? If you think that your hair is thinning and have a history of hair loss on either your Mother’s or Father’s side of the family, don’t ignore it. Make an appointment with your dermatologist to get evaluated and treated.
Do Asian Women get Alopecia?
Asian women do get alopecia, but traditionally rates have been lower than those of Caucasian or African-American women. (03) That number seems to be on the rise, though. Diet is believed to be a contributing factor.
Early research indicates that diets rich in vegetables, herbs, and soy may contribute to hair growth and health thanks to their anti-inflammatory nutrients. (04) The traditional Asian diet, loaded with fish and vegetables, meets that criteria.
Today’s modern Asian diet looks more like a typical American diet though, filled with processed foods. The fat, salt, and empty calories lead to higher BMI and blood sugar levels that have been linked to female pattern hair loss. (05)

What Treatments are Available to Women with Female Pattern Baldness?
Treatments for androgenic alopecia are designed with two goals in mind:
- Prevent further hair loss
- Stimulate hair growth
Sounds logical, right? Well, it is. Here are medications that dermatologists typically prescribe:
Retinol (Tretinoin)
Retinol is derived from Vitamin A and has been found to be effective for treating female pattern hair loss when used either alone or in combination with Minoxidil. (06) Retinol has been proven to stimulate growth and improve the absorption of other ingredients that promote hair growth.
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
Minoxidil, sold over-the-counter under the name Rogaine, is a hair regrowth treatment. It works by enlarging the hair follicles and elongating your hair’s growth phase. Minoxidil is available in both a topical foam and a pill. Although the foam is available in a two percent formula for women and a five percent formula for men, dermatologists often recommend the five percent for women to use for androgenic alopecia. Any hair growth realized while using Minoxidil can be lost if you stop using the product, so it is highly recommended to use it under the care of a licensed dermatologist.
Finasteride (Propecia)
Finasteride is a prescription medication that was initially designed to treat enlarged prostates. Because it prevents testosterone from converting into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the medicine is helpful for women with female pattern hair loss. (07) Finasteride is available as an oral medication and as a topical solution. Many women prefer topical to avoid potential side effects.
Dutasteride (Avodart)
Dutasteride is similar to Finasteride. Both medications prevent your body from converting testosterone into DHT, which causes female pattern baldness. Dutasteride is newer to the market and is used off-label for androgenic alopecia in women. Finasteride is highly effective for most women, but when stronger medications are required, Dutasteride is a good option. (08) Like Finasteride, Dutasteride is best for women who are not pregnant or thinking about becoming pregnant.
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
Spironolactone is an effective treatment for hormone-induced hair loss that is only prescribed to women. The medication blocks DHT production by simultaneously decreasing testosterone and increasing estrogen.
Data indicates that Spironolactone is highly effective for treating female pattern baldness. In a research study conducted, 74.3 percent of patients who were treated with Spironolactone reported stabilization or improvement in their hair loss. (09)
Oral Spironolactone can cause low blood pressure, drowsiness, and other side effects. Topical Spironolactone, which does not go through the digestive system and is less likely to induce side effects, is often prescribed and preferred. Topical Spironolactone is often compounded with Minoxidil to help your hair grow even faster and thicker.
Compounded Topical Treatments
If you’re not thrilled about using multiple products, all-in-one topical treatments that combine multiple medications into one are now available and can be more effective than using just one medication alone. (10) Popular combinations are:
- Finasteride, Minoxidil, and Retinol
- Minoxidil and Spironolactone
Many women appreciate the convenience and ease of applying just one formula twice a day.
With So Many Medications Available to Women With Androgenic Alopecia, How Do You Choose?
Are you confused about all of the different options? If so, that’s understandable since some of the DHT blocking medications work similarly. Thankfully, dermatologists have experience selecting the right medications for patients with female pattern hair loss. Your dermatologist will help you choose the right medication, dosage, and combination of medication based on the severity of your hair loss and your medical history.
Remember that treatment for female pattern hair loss isn’t one-size-fits-all. Different medications work for different women. It’s common to go through a trial process to see what works best for you.
Also, keep in mind that patience is key when treating androgenic alopecia. Medications work over time, so it may be a few months before you see a noticeable improvement, no matter which treatment you and your dermatologist choose.
Women With Androgenic Alopecia Often Need a Support System
Every woman deals with androgenic alopecia differently. My friend Barbara took her diagnosis in stride, but many women are devastated. Hair is a huge part of a woman’s identity, and losing it can take a toll on a woman’s confidence.
If you’re having trouble coping with your hair loss, resources are available to you. Best of all, some of the resources are free. Facebook has a closed group dedicated to females with androgenic alopecia. Members share information about their diagnosis and treatment plans. Sometimes, they’re just there to tell each other that it’s okay to be sad about their hair loss. Whether it’s on Facebook, another social media outlet, or in person, support groups are a good way to connect with others who are feeling the same way as you about your hair loss situation.
If you’re not in a good place mentally, make sure you contact a qualified psychologist or a psychiatrist. Depression and anxiety are common among women with female pattern hair loss. It’s important to seek help so you can regain your sense of self.
Resources:
(01) Name has been changed to protect confidentiality
(02) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/03/160304093239.htm
(03) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4560543/
(04) https://www.karger.com/Article/Fulltext/504786
(05) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4560543/
(06) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3771854/
(07) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7060023/
(08) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25382509/
(09) https://www.jaad.org/article/S0190-9622(15)01878-2/fulltext
(10) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4314881/